Symptoms
Fibroids do not always cause symptoms. Even though 20-40% of women have uterine fibroids, most do not notice them.
Only 10-20% of women with fibroids ever require treatment Depending on location, size and number of fibroids, a woman might experience the following
• Pelvic pain
• Pelvic pressure or heaviness
• Pain in the back or legs as the fibroids press on nerves that supply the pelvis and legs
• Pain during sexual intercourse
• Having to go to the bathroom often
• Abnormally enlarged abdomen
• Heavy, prolonged menstrual periods and unusual monthly bleeding, sometimes clots. This might leads to a condition called anaemia, or low blood counts.
Diagnosis
Fibroids usually shrink on their own after menopause. However, if you have symptoms related to your fibroids, you should see a doctor.
If you have large fibroids, your doctor may suspect this after physically examining you, but most fibroids are diagnosed by ultrasound. In some cases, when planning treatment, the doctor will use MRI to characterise the fibroids and assess their response to therapy.
Treatment
There are a number of treatments available, some of which will preserve your uterus and some of which will not. A hysterectomy is a surgery to remove the entire uterus. Future pregnancy is not possible. A myomectomy is a surgery to remove the fibroid but leave the uterus.
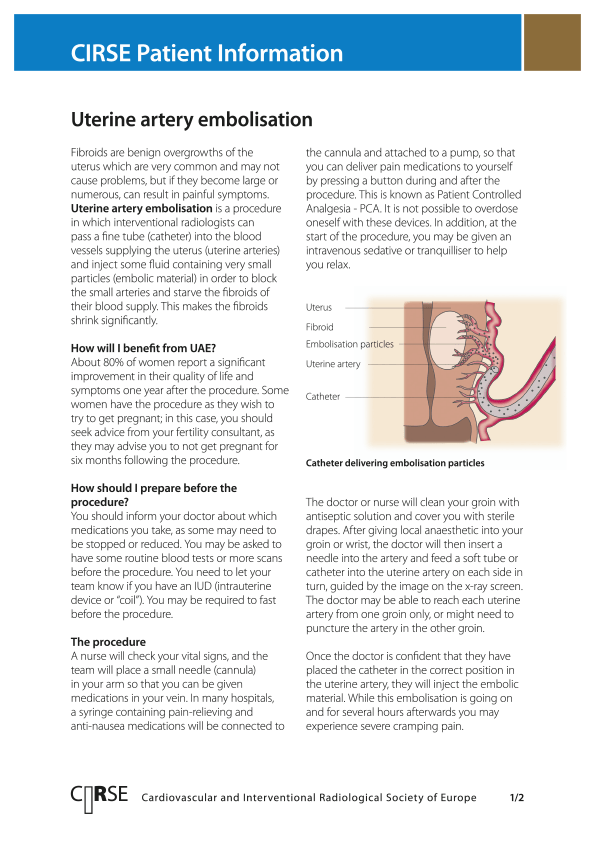
There are a few alternatives to the surgical option for the treatment of fibroids. The one minimally invasive with the best results is called uterine fibroid embolization or “UFE.” It is performed by a specialist called an interventional radiologist (IR).
The goal of UFE is to block the blood supply to the uterus through a small artery hole (uterine fibroid embolization.)
You also may be given hormonal treatments for the fibroids.
Choosing the most appropriate treatment depends on what symptoms you have, the impact of these symptoms on your quality of life, and whether you are trying to have a baby now or in the future.