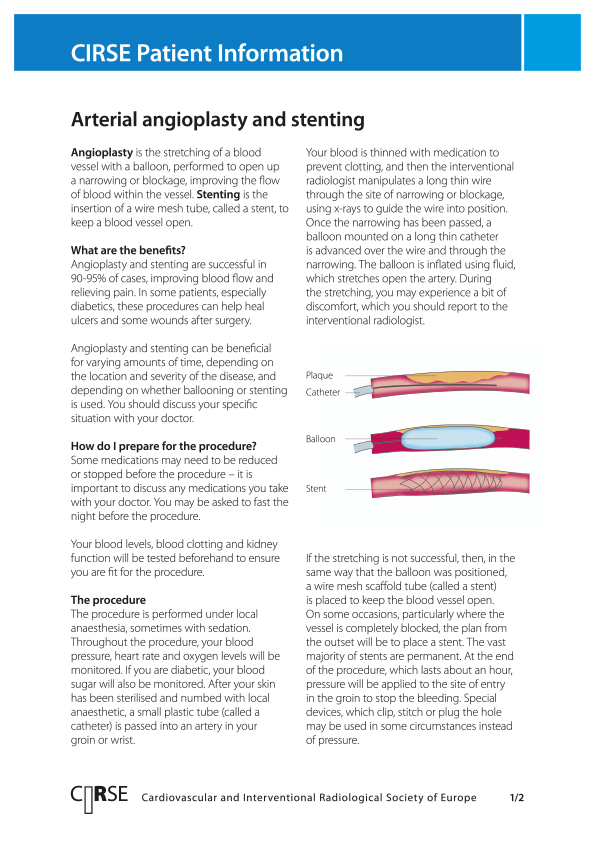
Overview
Arterial occlusive disease is a condition in which the arteries throughout the body gradually become narrowed. It can affect arms and legs. Often, patients who suffer from lower extremity arterial occlusive disease also have other conditions, such as carotid artery disease and heart disease. The condition is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
The major risk factors for arterial occlusive disease are age, high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides (a type of fat found in the blood), high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking and a history of plaque build-up in the arteries. Men are more likely than women to develop arterial occlusive disease.